Maintaining cardiovascular wellness is of paramount importance for overall health and well-being. While several factors contribute to heart health, emerging research has shed light on the potential role of Vitamin D in this regard. Vitamin D, often referred to as the "sunshine vitamin," plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including bone health, immune system regulation, and now, cardiovascular wellness. In this article, we will explore five key pieces of information about Vitamin D and its impact on heart health. Understanding these factors can help individuals make informed decisions about their cardiovascular well-being and potentially take steps towards maintaining a healthy heart.
1, Vitamin D Deficiency and Heart Disease.
Research has indeed suggested an association between vitamin D deficiency and an increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, including heart disease, heart attack, and stroke. While the exact mechanisms are not fully understood, there are several reasons why vitamin D is believed to play a role in maintaining a healthy cardiovascular system.
Vitamin D is primarily known for its role in maintaining bone health and regulating calcium absorption. However, it also has other important functions in the body, including regulating blood pressure, reducing inflammation, and modulating the immune system. These functions are believed to be relevant to cardiovascular health.
Low levels of vitamin D have been associated with increased blood pressure, which is a risk factor for heart disease. Vitamin D deficiency may also contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries. Plaque formation can restrict blood flow to the heart, leading to heart attacks and strokes.
Furthermore, vitamin D deficiency has been linked to chronic inflammation, which is thought to contribute to the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases. Inflammation plays a role in the initiation of atherosclerosis and can increase the risk of plaque rupture, leading to blood clots and cardiovascular events.
Although observational studies have found an association between low vitamin D levels and cardiovascular diseases, it is important to note that these studies do not establish a cause-and-effect relationship. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are needed to provide more definitive evidence regarding the impact of vitamin D supplementation on cardiovascular outcomes.
If you suspect you have a vitamin D deficiency or are concerned about your cardiovascular health, it is best to consult with a healthcare professional. They can assess your individual situation, conduct appropriate tests, and provide guidance on optimizing your vitamin D levels and managing your cardiovascular health.
2, Blood Pressure Regulation.
Adequate levels of vitamin D have been associated with the regulation of blood pressure. The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is an important pathway involved in blood pressure regulation, and vitamin D is believed to influence its functioning.
The RAS pathway involves the conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I by the enzyme renin. Angiotensin I is then converted to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor, by the enzyme angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). Angiotensin II causes blood vessels to narrow and promotes the release of aldosterone, a hormone that increases sodium and water reabsorption, leading to increased blood volume and higher blood pressure.
Vitamin D has been shown to play a role in modulating the RAS pathway. It can suppress the activity of renin, thus reducing the conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I. Additionally, vitamin D can inhibit the expression of ACE, which reduces the formation of angiotensin II. This dual effect of vitamin D on the RAS pathway can help maintain blood pressure within a healthy range.
Several observational studies have found an inverse relationship between vitamin D levels and blood pressure. Individuals with higher vitamin D levels tend to have lower blood pressure, while lower vitamin D levels are associated with higher blood pressure. However, it is important to note that the evidence from clinical trials regarding the effects of vitamin D supplementation on blood pressure has been mixed, with some studies showing a modest reduction in blood pressure and others finding no significant effect.
While vitamin D may play a role in blood pressure regulation, it is not the sole determinant, and other factors such as lifestyle, diet, genetics, and overall health also influence blood pressure levels. If you have concerns about your blood pressure or vitamin D status, it is best to consult with a healthcare professional who can evaluate your individual situation and provide appropriate guidance.
3, Reduced Inflammation.
Chronic inflammation is recognized as a contributing factor in the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases. Vitamin D has been found to possess anti-inflammatory properties, which may help reduce inflammation and lower the risk of heart-related conditions.
Inflammation plays a critical role in the development of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries. Inflammatory processes can initiate and promote the formation of plaque, leading to narrowing and hardening of the arteries. This can increase the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events.
Vitamin D has been shown to have immune-modulating effects and can help regulate the inflammatory response. It can inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), and promote the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-10 (IL-10). By modulating the balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory factors, vitamin D can help reduce systemic inflammation.
Moreover, vitamin D can also influence the function of immune cells involved in the inflammatory response. It can modulate the activity of immune cells, such as macrophages and T cells, which play key roles in the initiation and regulation of inflammation. By modulating the immune response, vitamin D may help mitigate chronic inflammation and potentially reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
However, it is important to note that while vitamin D has demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects in laboratory studies and observational studies have shown associations between vitamin D deficiency and increased inflammation, the clinical evidence regarding the specific impact of vitamin D supplementation on reducing inflammation in cardiovascular diseases is still limited. Further research, including randomized controlled trials, is needed to establish a direct cause-and-effect relationship between vitamin D supplementation, inflammation reduction, and cardiovascular outcomes.
If you have concerns about inflammation or cardiovascular health, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional who can evaluate your individual situation and provide appropriate guidance and treatment.
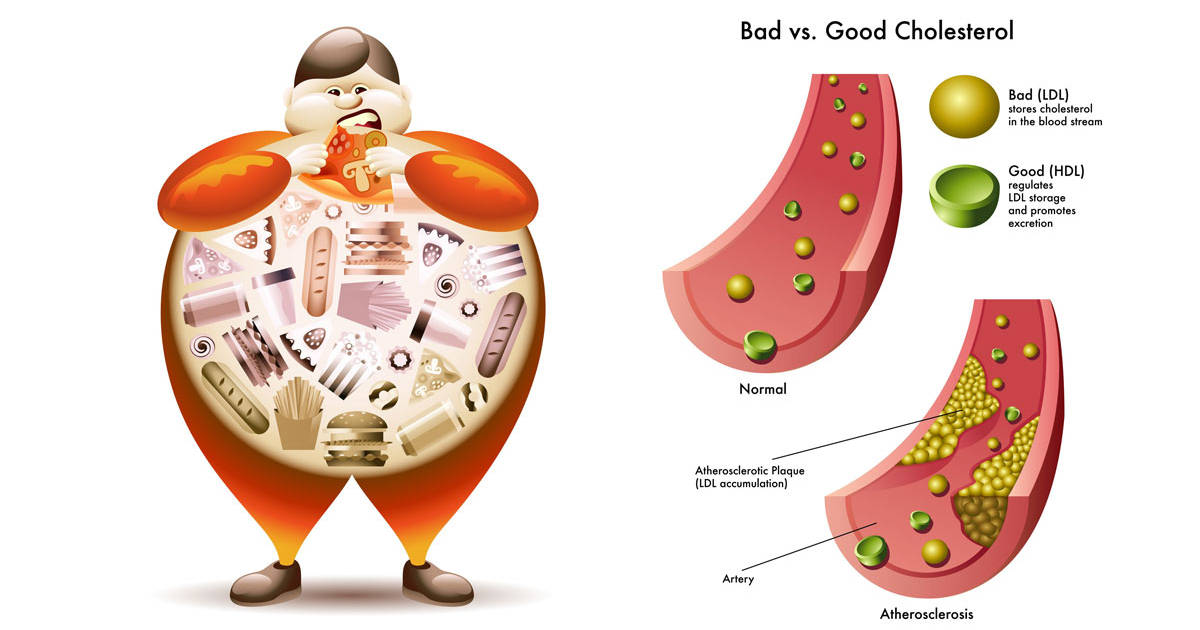
4, Improved Cholesterol Profile.
While maintaining healthy levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol is beneficial for heart health, the relationship between vitamin D supplementation and improvements in the lipid profile, including HDL cholesterol levels, is still not fully understood.
Some studies have suggested a potential association between vitamin D supplementation and improvements in the lipid profile, including increasing HDL cholesterol levels. However, the evidence is limited and inconsistent. Many of the studies conducted so far have been observational or small-scale, and findings have been mixed.
It's important to note that the effects of vitamin D supplementation on lipid profile may vary depending on individual factors, such as baseline vitamin D levels, overall health status, and the presence of underlying medical conditions. Additionally, the optimal dosage, duration, and specific populations that may benefit from vitamin D supplementation for lipid profile improvements have not been clearly established.
If you are concerned about your lipid profile or heart health, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional who can assess your specific situation and provide appropriate guidance. They can help you develop a comprehensive approach to managing your lipid profile and reducing cardiovascular risk, which may include lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and potentially other medications if needed.
5, Heart Failure Prevention.
Adequate vitamin D levels have been associated with a reduced risk of heart failure. Heart failure is a condition characterized by the heart's inability to pump blood effectively, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, and fluid retention.
Several studies have examined the association between vitamin D levels and the incidence of heart failure. These studies have consistently shown that individuals with higher vitamin D levels tend to have a lower risk of developing heart failure compared to those with lower levels of vitamin D.
Vitamin D may have several mechanisms that contribute to its potential protective effect against heart failure. Firstly, vitamin D plays a role in regulating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), which helps regulate blood pressure and fluid balance. Dysregulation of the RAAS system can contribute to the development and progression of heart failure. Vitamin D's influence on the RAAS system may help maintain cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of heart failure.
Secondly, vitamin D has been shown to have anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic properties, which may help prevent or reduce the cardiac remodeling and fibrosis associated with heart failure. Chronic inflammation and fibrosis can lead to structural changes in the heart muscle, impairing its function over time.
While the observational studies have consistently found an association between higher vitamin D levels and a reduced risk of heart failure, it is important to note that these studies cannot establish a cause-and-effect relationship. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are necessary to determine the potential benefits of vitamin D supplementation in preventing or managing heart failure.
If you are concerned about heart failure or vitamin D levels, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional. They can evaluate your individual situation, conduct appropriate tests, and provide guidance on optimizing your vitamin D levels and managing your cardiovascular health.
In conclusion, Vitamin D has emerged as a potential ally in maintaining cardiovascular wellness. Adequate levels of Vitamin D have been associated with a lower risk of heart disease, regulated blood pressure, reduced inflammation, improved cholesterol profile, and even a decreased risk of heart failure. While more research is needed to fully understand the complex relationship between Vitamin D and heart health, the existing evidence suggests that ensuring optimal Vitamin D levels may have significant benefits for cardiovascular wellness. However, it is important to note that Vitamin D should be considered as part of a holistic approach to heart health, alongside other lifestyle factors such as a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and medical guidance. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for personalized advice and recommendations regarding Vitamin D supplementation and overall heart health. By staying informed and taking proactive steps, individuals can prioritize their cardiovascular wellness and work towards a healthier heart.



Comments
Post a Comment