Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a vital nutrient that plays numerous roles in maintaining overall health. Besides its well-known benefits in boosting the immune system and preventing scurvy, emerging research suggests that vitamin C may possess potential anti-cancer properties. In this article, we will explore five helpful pieces of information about the potential anti-cancer properties of vitamin C. From its antioxidant activity and immune system support to its role in collagen synthesis and enhancing chemotherapy effectiveness, vitamin C demonstrates promising attributes in the fight against cancer. However, it is important to note that further research is needed, and it should not be considered a standalone treatment for cancer.
1, Antioxidant activity.
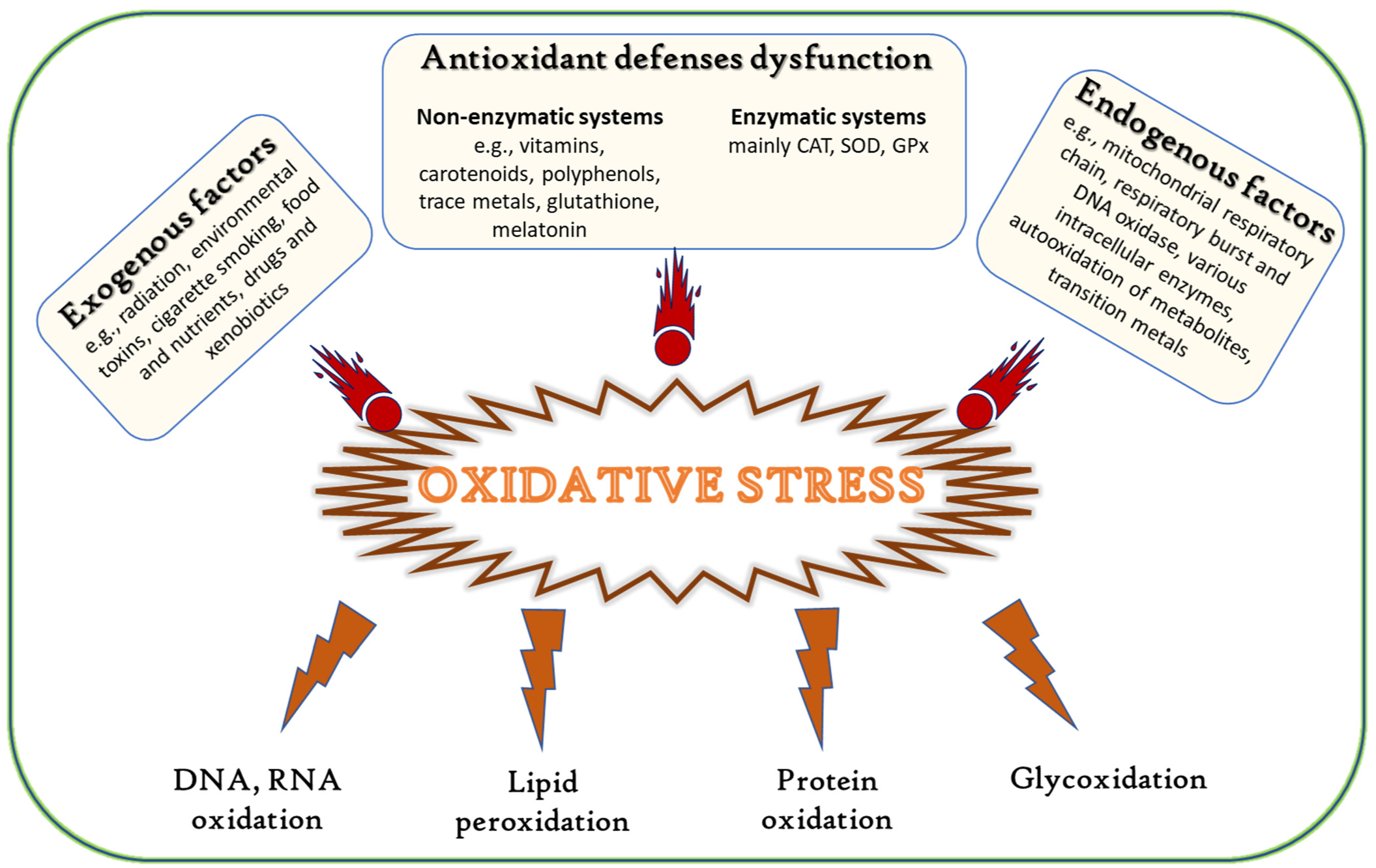
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a powerful antioxidant that plays a crucial role in protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that have an unpaired electron, making them highly reactive. They can be generated through normal metabolic processes in the body or can be introduced from external sources such as exposure to pollutants, radiation, or certain chemicals.
When free radicals accumulate in the body, they can cause oxidative stress, which can lead to cellular damage and contribute to various diseases, including cancer. Oxidative stress can cause DNA damage and mutations, disrupt normal cell signaling, and promote inflammation, all of which are factors associated with cancer development and progression.
Vitamin C acts as an antioxidant by donating an electron to stabilize and neutralize free radicals, thereby preventing them from damaging cells and DNA. Additionally, vitamin C can regenerate other antioxidants such as vitamin E, further enhancing the overall antioxidant defense system in the body.
Several studies have suggested a potential link between vitamin C intake and a reduced risk of certain types of cancer. However, it's important to note that while vitamin C is beneficial for overall health and may play a role in reducing cancer risk, it should not be considered a standalone treatment for cancer. A well-rounded diet rich in fruits and vegetables, including those high in vitamin C, along with other healthy lifestyle choices, can contribute to a lower risk of cancer and improved overall health. If you have specific concerns about cancer prevention or treatment, it's always best to consult with a healthcare professional.
2, Immune system support.
Vitamin C is indeed essential for maintaining a healthy immune system. It has several roles in supporting immune function, including:
Enhancing White Blood Cell Function: Vitamin C is involved in the production and function of various types of white blood cells, particularly lymphocytes and phagocytes. Lymphocytes, such as T cells and B cells, play a crucial role in immune responses, including recognizing and eliminating abnormal cells, such as cancer cells. Phagocytes, including neutrophils and macrophages, are responsible for engulfing and destroying pathogens and cellular debris.
Stimulating Collagen Production: Collagen is a protein that forms the structural framework of various tissues, including the skin, blood vessels, and organs. Vitamin C is necessary for the synthesis of collagen, which is vital for maintaining the integrity of skin and mucosal barriers that act as the body's first line of defense against pathogens.
Antioxidant Activity: As mentioned earlier, vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that helps neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress. By doing so, it protects immune cells from damage and maintains their optimal function.
Enhancing Iron Absorption: Vitamin C aids in the absorption of non-heme iron from plant-based food sources. Iron is essential for the proper functioning of immune cells, and vitamin C's role in enhancing iron absorption helps support adequate iron levels for immune function.
A robust immune system is vital in recognizing and eliminating abnormal cells, including potential cancer cells, before they develop into tumors. While vitamin C is beneficial for immune health, it's important to note that it works in conjunction with other nutrients, and a balanced diet along with a healthy lifestyle is crucial for overall immune system support. If you have specific concerns about your immune system or cancer prevention, it's always best to consult with a healthcare professional.
3, Collagen synthesis.
Vitamin C is essential for the synthesis of collagen, which is a key structural protein in the body. Collagen provides strength, stability, and support to various tissues, including skin, tendons, ligaments, cartilage, blood vessels, and organs.
In the context of wound healing, collagen is particularly important. When tissue damage occurs, collagen plays a critical role in the repair process. It helps form a framework for new tissue growth, promotes the migration of cells involved in wound healing, and contributes to the development of granulation tissue. Vitamin C's role in collagen synthesis is crucial for proper wound healing and the formation of healthy scar tissue.
Regarding cancer, collagen and its role in maintaining the integrity of blood vessels are relevant. Cancer cells can invade nearby tissues and spread to distant sites in the body through a process called metastasis. Angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, is a crucial step in this process as it provides the necessary nutrients and oxygen for tumor growth.
Collagen helps maintain the integrity and stability of blood vessels, which can play a role in inhibiting the spread of cancer cells. A strong and intact network of blood vessels can help prevent the formation of new blood vessels in tumors, thereby limiting their growth and potential for metastasis.
While collagen itself does not directly fight cancer cells, its role in wound healing and maintaining blood vessel integrity contributes to an environment that may be less conducive to cancer development and progression.
It's important to note that the relationship between collagen, vitamin C, and cancer is complex and multifaceted. While vitamin C's role in collagen synthesis is significant, it is just one aspect of cancer development and prevention. A comprehensive approach to cancer prevention and treatment involves various factors, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, and regular screenings as recommended by healthcare professionals.
4, Enhancing chemotherapy effectiveness.
The potential use of high-dose intravenous vitamin C (IVC) in combination with chemotherapy has been an area of interest in cancer research. While further studies are still needed to establish its effectiveness and optimal dosages, some research suggests that high-dose vitamin C may enhance the efficacy of certain chemotherapy drugs.
One proposed mechanism of action is that high levels of vitamin C, when administered intravenously, can generate hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in the extracellular space. Hydrogen peroxide is a reactive oxygen species that can induce oxidative stress in cancer cells. Normal cells have mechanisms to deal with oxidative stress, but cancer cells often have impaired antioxidant defense systems, making them more vulnerable to the toxic effects of hydrogen peroxide.
The increased levels of hydrogen peroxide can potentially promote selective toxicity towards cancer cells, leading to increased sensitivity to chemotherapy drugs. It is believed that the combination of high-dose vitamin C and chemotherapy may have a synergistic effect, improving the therapeutic outcomes.
However, it's important to note that the effectiveness of high-dose vitamin C as an adjunct therapy to chemotherapy may depend on several factors, such as the type of cancer, the specific chemotherapy drugs used, the dosage and administration protocol of vitamin C, and individual patient characteristics. Further research is needed to determine the optimal conditions, dosages, and potential side effects of this approach.
It's also crucial to emphasize that high-dose intravenous vitamin C as a complementary therapy should only be administered under the supervision and guidance of healthcare professionals. It's not recommended to rely solely on high-dose vitamin C or any other alternative therapy as a substitute for standard cancer treatments. Cancer treatment decisions should always be made in consultation with qualified medical professionals based on individual circumstances and in consideration of the available scientific evidence.
5, Reduced cancer risk.
several epidemiological studies have suggested an association between higher vitamin C intake and a reduced risk of certain types of cancer. While the exact mechanisms are not fully understood, there are several potential ways in which vitamin C may contribute to the reduced risk of cancer:
Antioxidant Activity: Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that helps neutralize free radicals, which can cause cellular damage and contribute to the development of cancer. By reducing oxidative stress, vitamin C may help protect cells from DNA damage and mutations, which are associated with cancer initiation.
Immune System Support: As mentioned earlier, vitamin C plays a crucial role in supporting a healthy immune system. A robust immune system is vital in recognizing and eliminating abnormal cells, including cancer cells, before they develop into tumors. By stimulating immune cell production and function, vitamin C may enhance the body's ability to fight against cancerous cells.
DNA Repair: Vitamin C is involved in DNA repair mechanisms, which help maintain the integrity of the genetic material. Proper DNA repair is crucial for preventing the accumulation of mutations that can lead to cancer development.
Collagen Synthesis and Tissue Integrity: Vitamin C's role in collagen synthesis is not only important for wound healing but also for maintaining the integrity of various tissues, including the lining of the digestive tract. This may play a role in reducing the risk of certain cancers, such as stomach, colon, and esophageal cancers.
It's important to note that while epidemiological studies have shown associations between higher vitamin C intake and reduced cancer risk, these studies cannot establish a cause-and-effect relationship. Other lifestyle and dietary factors may also contribute to the observed correlations. Further research, including randomized controlled trials and mechanistic studies, is needed to better understand the specific effects of vitamin C on cancer prevention.
Maintaining a well-rounded diet that includes a variety of fruits and vegetables, which are natural sources of vitamin C, is generally recommended for overall health and may contribute to a lower risk of certain types of cancer. However, it's important to remember that individual factors and lifestyle choices, along with regular screenings and consultations with healthcare professionals, play a significant role in cancer prevention and overall well-being.
In conclusion, vitamin C holds considerable promise in its potential anti-cancer properties. Its antioxidant activity and immune system support contribute to reducing the risk of cancer development and progression. Furthermore, its involvement in collagen synthesis and ability to enhance chemotherapy effectiveness highlight its multifaceted role in combating cancer. However, it is crucial to emphasize that vitamin C should not be relied upon as a standalone treatment for cancer, but rather as a part of a comprehensive approach that includes proper medical diagnosis, treatment, and management. As research continues to unveil the intricacies of vitamin C's effects on cancer, it is essential to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized guidance and treatment strategies tailored to individual needs.



Comments
Post a Comment