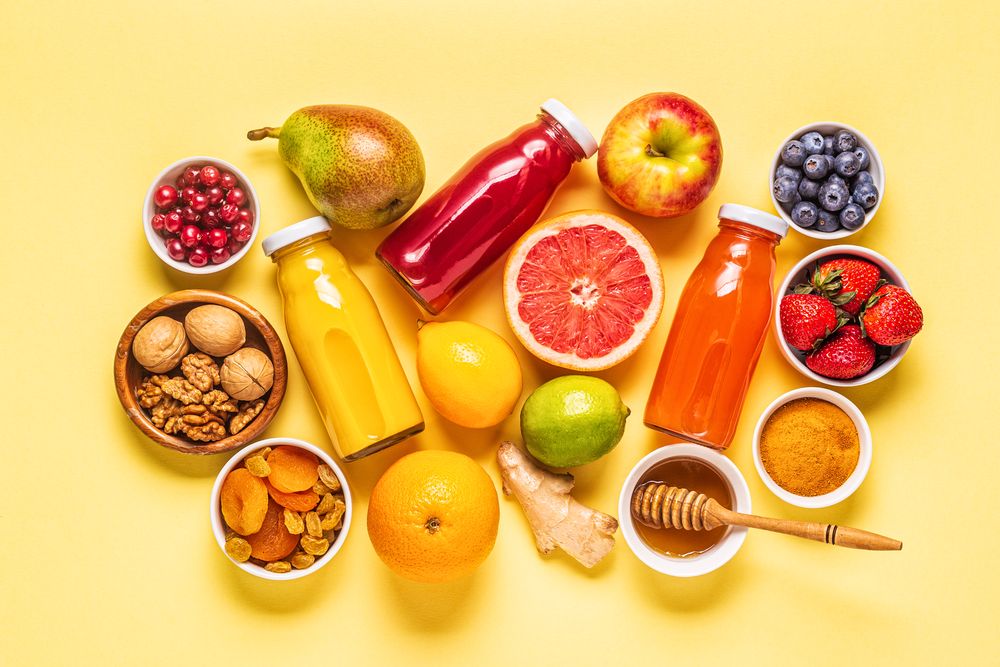
Maintaining good digestive health is crucial for overall well-being, and one of the most effective ways to support a healthy digestive system is by incorporating fruits and vegetables into your diet. These natural powerhouses offer a multitude of benefits that can keep your digestive system functioning optimally. From their high fiber content to their nutrient-rich profiles and natural digestive enzymes, fruits and vegetables play a significant role in promoting digestive health. In this article, we will explore the top five helpful pieces of information about the benefits of fruits and vegetables for your digestive system.
1, High Fiber Content.
Fruits and vegetables are indeed excellent sources of dietary fiber, which is an essential component of a healthy diet. Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that cannot be digested by the human body. Instead, it passes through the digestive system relatively intact, providing several benefits.
One of the primary roles of dietary fiber is to add bulk to the stool, which helps promote regular bowel movements. This can prevent or alleviate constipation, a condition characterized by infrequent or difficult passage of stool. By increasing the size and softness of the stool, fiber makes it easier to pass through the intestines and reduces the strain during bowel movements.
Moreover, dietary fiber acts as a prebiotic, serving as nourishment for beneficial gut bacteria. These bacteria reside in the large intestine and play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy digestive system. When fiber reaches the colon, it undergoes fermentation by gut bacteria, producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) as a byproduct. SCFAs provide energy to the cells lining the colon and help maintain their health.
In addition to promoting digestive health, a high-fiber diet has other benefits. It can help regulate blood sugar levels by slowing down the absorption of glucose in the bloodstream, which is particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes. Fiber-rich foods also tend to be more filling, making them useful for weight management by promoting satiety and reducing overeating.
To ensure an adequate intake of dietary fiber, it is recommended to consume a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. The recommended daily intake of fiber varies depending on age and gender but generally ranges from 25 to 38 grams for adults. It's important to gradually increase fiber intake to allow the digestive system to adjust and to drink plenty of water to prevent potential discomfort.
2, Nutrient-rich.
Fruits and vegetables are nutrient powerhouses, providing a wide range of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall digestive function and health.
Vitamin C, which is abundant in citrus fruits like oranges and lemons, plays a crucial role in the synthesis of collagen. Collagen is a protein that helps maintain the integrity and strength of the digestive tract, including the stomach and intestines. By supporting the health of the digestive lining, vitamin C promotes proper nutrient absorption and protects against potential damage.
Antioxidants, such as beta-carotene, are compounds found in various fruits and vegetables, including carrots, sweet potatoes, and leafy greens. These antioxidants help protect the gut lining from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. Oxidative stress can lead to inflammation and damage to the cells in the digestive system. By neutralizing free radicals, antioxidants contribute to the overall health of the digestive tract and help maintain its proper function.
In addition to vitamin C and beta-carotene, fruits and vegetables provide a wide array of other vitamins and minerals that are essential for digestive health. For example, B vitamins, including thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, and folate, are important for energy production and maintaining a healthy nervous system, including the nerves that control digestion. Minerals like potassium, magnesium, and calcium are also found in abundance in fruits and vegetables and play various roles in maintaining digestive health.
It's important to consume a diverse range of fruits and vegetables to ensure an adequate intake of these essential nutrients. Different fruits and vegetables offer different vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, so incorporating a variety of colors and types into your diet is beneficial. Remember to include whole fruits and vegetables rather than relying solely on juices, as whole foods provide additional fiber and nutrients that may be lost in the juicing process.
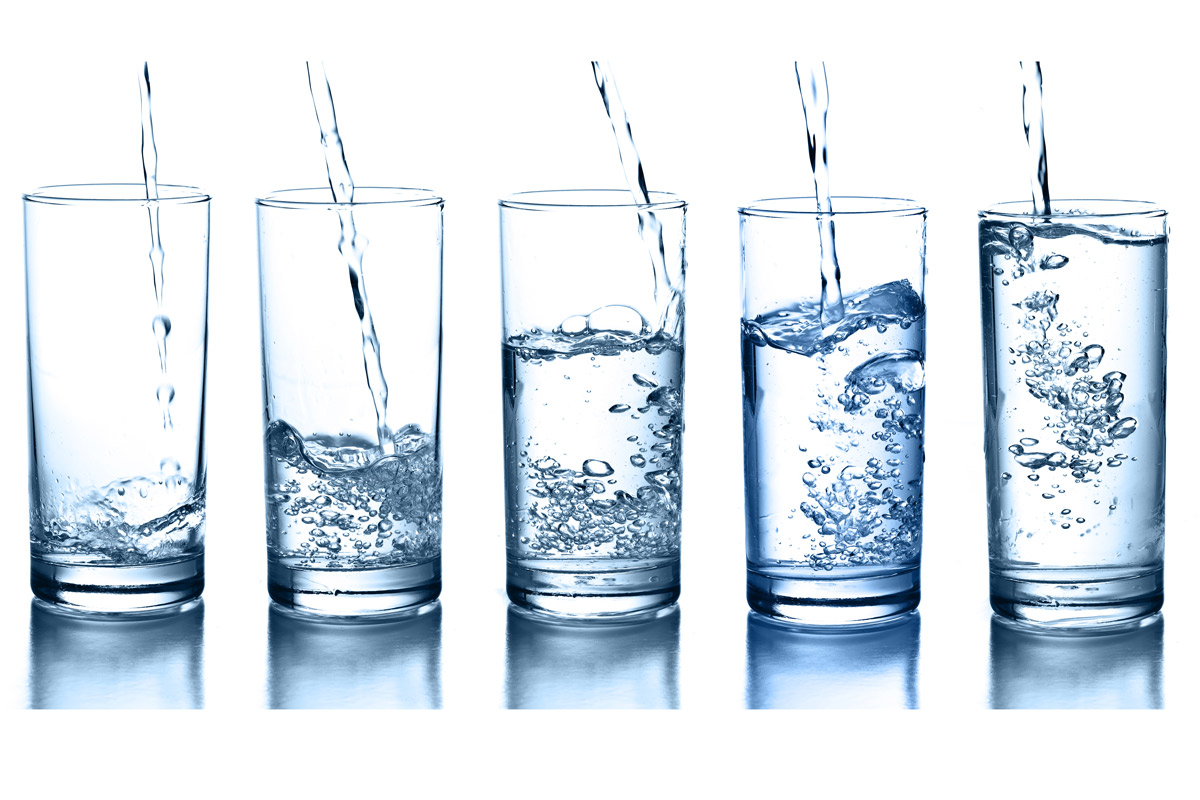
3, Hydration.
Hydration is crucial for maintaining optimal digestive health, and many fruits and vegetables can help in that regard. These hydrating foods contain high water content, which contributes to the body's overall hydration levels.
Proper hydration is essential for softening the stool and preventing constipation. When the body is dehydrated, the colon absorbs more water from the stool, making it harder and more difficult to pass. By consuming fruits and vegetables with high water content, you can help maintain adequate hydration and support regular bowel movements.
Cucumber is an excellent example of a hydrating fruit. It contains about 96% water, making it an incredibly refreshing and hydrating choice. Including cucumber in your diet can contribute to your overall hydration status and promote a healthy digestive system.
Watermelon is another fruit with high water content, at around 92% water. It not only helps quench thirst but also provides essential nutrients like vitamins A and C. Consuming watermelon can be a delicious and hydrating way to support digestive health.
Berries, such as strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries, are also hydrating fruits that offer numerous benefits for digestion. They contain a good amount of water, along with fiber and antioxidants. The fiber in berries adds bulk to the stool, promoting regular bowel movements, while antioxidants help protect the digestive system from oxidative damage.
Apart from these examples, other fruits and vegetables with high water content include melons (such as cantaloupe and honeydew), citrus fruits (like oranges and grapefruits), and leafy greens (such as lettuce and spinach).
Remember that while consuming hydrating fruits and vegetables is beneficial, it's also important to drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day to maintain optimal hydration levels. This combination of hydrating foods and proper water intake can contribute to a healthy digestive system and overall well-being.
4, Natural Digestive Enzymes.
Certain fruits and vegetables contain natural enzymes that can aid in the digestion of food. These enzymes can help break down specific nutrients and promote better digestion, alleviating symptoms of indigestion.
Pineapple is well-known for containing an enzyme called bromelain. Bromelain is a mixture of enzymes, including proteases, which are responsible for breaking down proteins. By assisting in protein digestion, bromelain can help improve the breakdown of dietary proteins in the stomach and small intestine. This enzyme can be particularly beneficial for individuals who have difficulty digesting proteins or experience symptoms of bloating or discomfort after protein-rich meals.
Papaya is another fruit that contains a digestive enzyme called papain. Papain is also a protease enzyme that aids in the breakdown of proteins. It helps to break down complex protein structures into smaller peptides and amino acids, facilitating their absorption in the digestive system. Consuming papaya or papaya enzyme supplements may help improve protein digestion and alleviate symptoms of indigestion, such as bloating or gas.
In addition to bromelain and papain, other fruits and vegetables may contain natural enzymes that support digestion. For example, kiwi fruit contains actinidin, an enzyme that assists in the breakdown of proteins. Mango contains enzymes like amylases, which help break down carbohydrates, and proteases that aid in protein digestion.
It's important to note that while these natural enzymes can be beneficial for digestion, their effects may vary among individuals. Some people may experience noticeable improvements in digestion after consuming these fruits, while others may not notice a significant difference. It's always a good idea to listen to your body and observe how it responds to different foods.
Incorporating fruits like pineapple, papaya, kiwi, and mango into your diet can be a delicious way to potentially enhance digestion. However, if you have specific digestive concerns or conditions, it's best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
5, Gut Microbiome Support.
Fruits and vegetables play a significant role in supporting a healthy gut microbiome. The gut microbiome refers to the vast community of microorganisms, including bacteria, that reside in the intestines. These microorganisms have a symbiotic relationship with our bodies and play a crucial role in digestion, nutrient absorption, immune function, and overall health.
Fiber-rich fruits and vegetables serve as prebiotics, which are types of dietary fibers that provide nourishment for beneficial gut bacteria. Prebiotics act as fuel for these bacteria, allowing them to grow and thrive. As these bacteria ferment the dietary fiber, they produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as butyrate, acetate, and propionate, as byproducts. SCFAs provide energy to the cells lining the colon and help maintain a healthy gut environment.
By consuming a variety of fruits and vegetables, especially those high in fiber, you can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in your gut. This can help maintain a balanced gut microbiome, which is associated with numerous health benefits, including improved digestion, enhanced immune function, and even mental well-being.
Incorporating a wide range of colorful fruits and vegetables into your diet can provide a diverse array of nutrients and fiber types, nourishing different populations of gut bacteria. It's important to consume both soluble and insoluble fiber, as they have distinct benefits for gut health. Soluble fiber, found in fruits like apples and berries, forms a gel-like substance and can help regulate bowel movements. Insoluble fiber, present in vegetables like broccoli and leafy greens, adds bulk to the stool and supports regularity.
Remember that gradually increasing your fiber intake and staying adequately hydrated are key to optimizing the benefits of fiber for your gut microbiome. It's also important to note that individual responses to dietary changes can vary, so it's always a good idea to listen to your body and make adjustments as needed.
Overall, by including a variety of fiber-rich fruits and vegetables in your diet, you can support a healthy gut microbiome and contribute to better digestive health and overall well-being.
Incorporating fruits and vegetables into your daily diet can have a remarkable impact on your digestive health. Their high fiber content, nutrient-rich composition, natural digestive enzymes, hydration properties, and support for a healthy gut microbiome make them invaluable allies in maintaining optimal digestive function. By including a variety of fruits and vegetables in your meals, you can ensure that you are providing your body with essential nutrients and promoting a well-balanced digestive system. So, make it a habit to embrace the vibrant colors and flavors of nature's bounty and enjoy the tremendous benefits that fruits and vegetables offer for your digestive health.




Comments
Post a Comment