Maintaining healthy bones and preventing arthritis are crucial aspects of overall well-being. Calcium and vitamin D are two essential nutrients that play a vital role in supporting bone health and preventing the onset of arthritis. Understanding the importance of these nutrients and incorporating calcium and vitamin D-rich foods into our diets can help strengthen bones, reduce the risk of osteoporosis, and potentially prevent certain types of arthritis. In this article, we will explore the top five helpful pieces of information about calcium and vitamin D-rich foods for bone health and arthritis prevention.
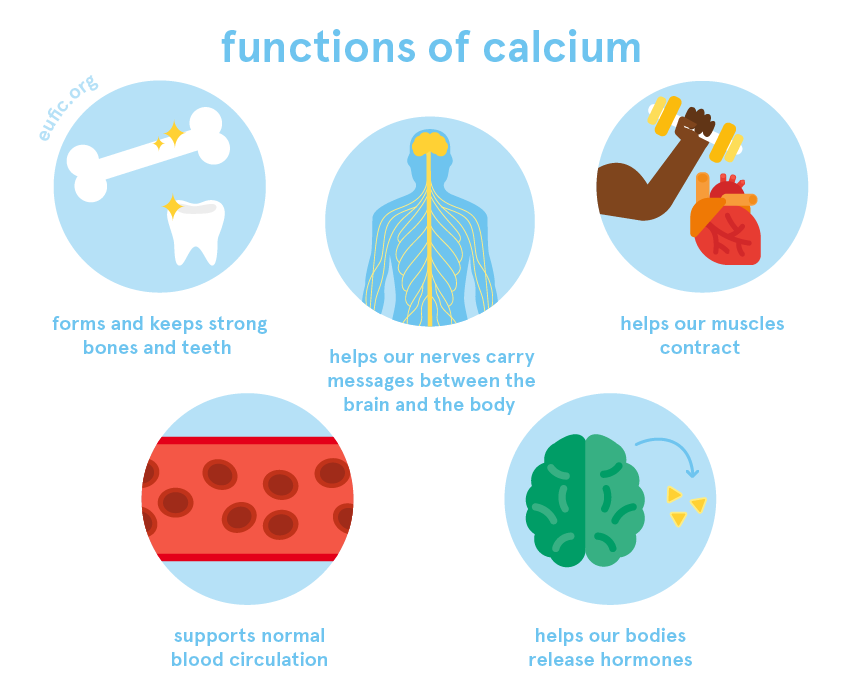
1, Importance of Calcium.
Calcium is indeed a crucial mineral for maintaining overall bone health and preventing conditions like osteoporosis. It plays a vital role in various physiological processes throughout the body. Here are some key points highlighting the importance of calcium:
Bone Health: Calcium is a primary component of bones and teeth. It provides structural support and helps maintain their strength and density. Sufficient calcium intake is essential during childhood and adolescence when bone formation is at its peak. It also becomes increasingly important during adulthood to maintain bone mass and prevent age-related bone loss.
Osteoporosis Prevention: Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by low bone density and increased risk of fractures. Consuming enough calcium throughout life, combined with other factors like physical activity and vitamin D intake, can help reduce the risk of osteoporosis later in life.
Muscle Function: Calcium is involved in muscle contraction and relaxation. When a muscle receives a signal to contract, calcium ions are released, allowing the muscle fibers to shorten. Adequate calcium levels ensure proper muscle function, including the heart muscle.
Nerve Transmission: Calcium is crucial for the transmission of nerve impulses throughout the body. It plays a role in releasing neurotransmitters, which facilitate communication between nerve cells.
Blood Clotting: Calcium is necessary for the clotting of blood. When there is an injury or damage to blood vessels, calcium is released, triggering a cascade of events that form a blood clot, preventing excessive bleeding.
Hormone Secretion: Calcium is involved in the secretion of various hormones and enzymes. It plays a role in the regulation of several bodily processes, including hormone release from glands.
Dental Health: Calcium is essential for maintaining strong teeth. It helps in the development and mineralization of tooth enamel, which protects against tooth decay and cavities.
It's important to note that while calcium is crucial, it is best obtained through a balanced diet rather than relying solely on supplements. Good dietary sources of calcium include dairy products, leafy green vegetables, fortified plant-based milk, tofu, almonds, and sardines, among others. The recommended daily intake of calcium varies depending on age and gender, so it's best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
2, Vitamin D and Calcium Synergy.
You've highlighted an essential point about the synergy between vitamin D and calcium. Vitamin D plays a critical role in the absorption, utilization, and regulation of calcium in the body. Here's how vitamin D and calcium work together:
Calcium Absorption: Vitamin D helps enhance the absorption of calcium from the digestive system into the bloodstream. Without sufficient vitamin D, the body may struggle to absorb an adequate amount of calcium from the diet, even if the calcium intake is sufficient. Vitamin D promotes the synthesis of a protein called calbindin, which facilitates calcium absorption in the intestines.
Calcium Utilization: Once calcium is absorbed into the bloodstream, vitamin D helps regulate calcium levels to ensure its optimal utilization throughout the body. Vitamin D promotes the deposition of calcium into bones and teeth, supporting bone mineralization and strength.
Parathyroid Hormone Regulation: Vitamin D helps regulate the production and release of parathyroid hormone (PTH), which plays a crucial role in maintaining calcium balance. When blood calcium levels are low, PTH is released, stimulating the release of calcium from bones and increasing calcium absorption from the intestine. Vitamin D helps suppress excessive PTH release and supports the maintenance of appropriate calcium levels.
Bone Health: Vitamin D and calcium work together to support bone health. While calcium provides the structural component of bones, vitamin D helps ensure that calcium is properly absorbed and utilized for bone formation and mineralization. Adequate levels of both nutrients are necessary for optimal bone density and strength, reducing the risk of fractures and conditions like osteoporosis.
To ensure optimal benefits, it is recommended to have adequate intake of both calcium and vitamin D. Good dietary sources of vitamin D include fatty fish (such as salmon and mackerel), fortified dairy products, fortified plant-based milk, egg yolks, and exposure to sunlight, which triggers vitamin D synthesis in the skin. However, it may be challenging to obtain sufficient vitamin D from diet and sunlight alone, especially in regions with limited sun exposure. In such cases, vitamin D supplements may be recommended by healthcare professionals to meet the recommended daily intake. It's important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage based on individual needs and circumstances.
3, Good Sources of Calcium.
A diverse range of foods can provide adequate calcium intake for individuals who may have dietary restrictions or preferences. Here's a breakdown of the good sources of calcium you mentioned:
Dairy Products: Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt are well-known for their high calcium content. They are easily accessible and widely consumed sources of calcium.
Leafy Green Vegetables: Leafy greens such as spinach, kale, and collard greens are not only rich in vitamins and minerals but also contain significant amounts of calcium. They are great options for individuals who prefer plant-based sources of calcium.
Almonds: Almonds are a nutritious nut and provide a good amount of calcium. They make for a convenient and tasty calcium-rich snack.
Tofu: Tofu, made from soybean curds, is an excellent source of calcium, especially for those following a vegetarian or vegan diet.
Sesame Seeds: Sesame seeds are a versatile addition to various dishes and provide a notable amount of calcium.
Canned Fish with Edible Bones: Certain canned fish, like sardines and salmon, are rich in calcium due to their edible bones. These bones are soft and safe to consume, adding to the calcium content of the fish.
In addition to these sources, there are other calcium-fortified products available in the market, such as fortified plant-based milk (e.g., almond milk, soy milk) and fortified orange juice. These options can be beneficial for individuals with lactose intolerance or those who prefer non-dairy alternatives.
Maintaining a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of calcium-rich foods can help ensure adequate calcium intake. Remember that the recommended daily intake of calcium may vary depending on age, gender, and life stage, so it's always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized dietary recommendations.
4, Vitamin D-Rich Foods.
While sunlight is a primary source of vitamin D synthesis in the body, certain foods can also contribute to vitamin D intake. Here are some vitamin D-rich food sources:
Fatty Fish: Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and tuna are among the best natural food sources of vitamin D. They are not only delicious but also provide significant amounts of this essential nutrient.
Fortified Dairy Products: Many dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese are often fortified with vitamin D. Checking the labels can help identify fortified options that provide an additional boost of vitamin D.
Fortified Plant-Based Milk: Plant-based milk alternatives, such as soy milk, almond milk, or oat milk, are often fortified with vitamin D to match the nutritional profile of cow's milk. These options can be suitable for individuals who follow a vegan or lactose-free diet.
Egg Yolks: Egg yolks contain small amounts of vitamin D. Including eggs in your diet, especially the yolks, can contribute to your vitamin D intake.
UV-Exposed Mushrooms: Certain mushrooms, such as shiitake or maitake, when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light during growth or processing, can naturally increase their vitamin D content. These mushrooms are becoming more widely available and can be a good option for plant-based sources of vitamin D.
It's important to note that while these food sources can contribute to vitamin D intake, it may still be challenging to obtain sufficient vitamin D from diet alone, particularly for individuals living in regions with limited sunlight exposure. In such cases, vitamin D supplementation may be recommended by healthcare professionals to meet the recommended daily intake. Vitamin D supplements are available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and liquid drops. Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage based on your individual needs and circumstances.
Remember, achieving optimal vitamin D levels is a combination of sunlight exposure, dietary intake, and, if necessary, supplementation.
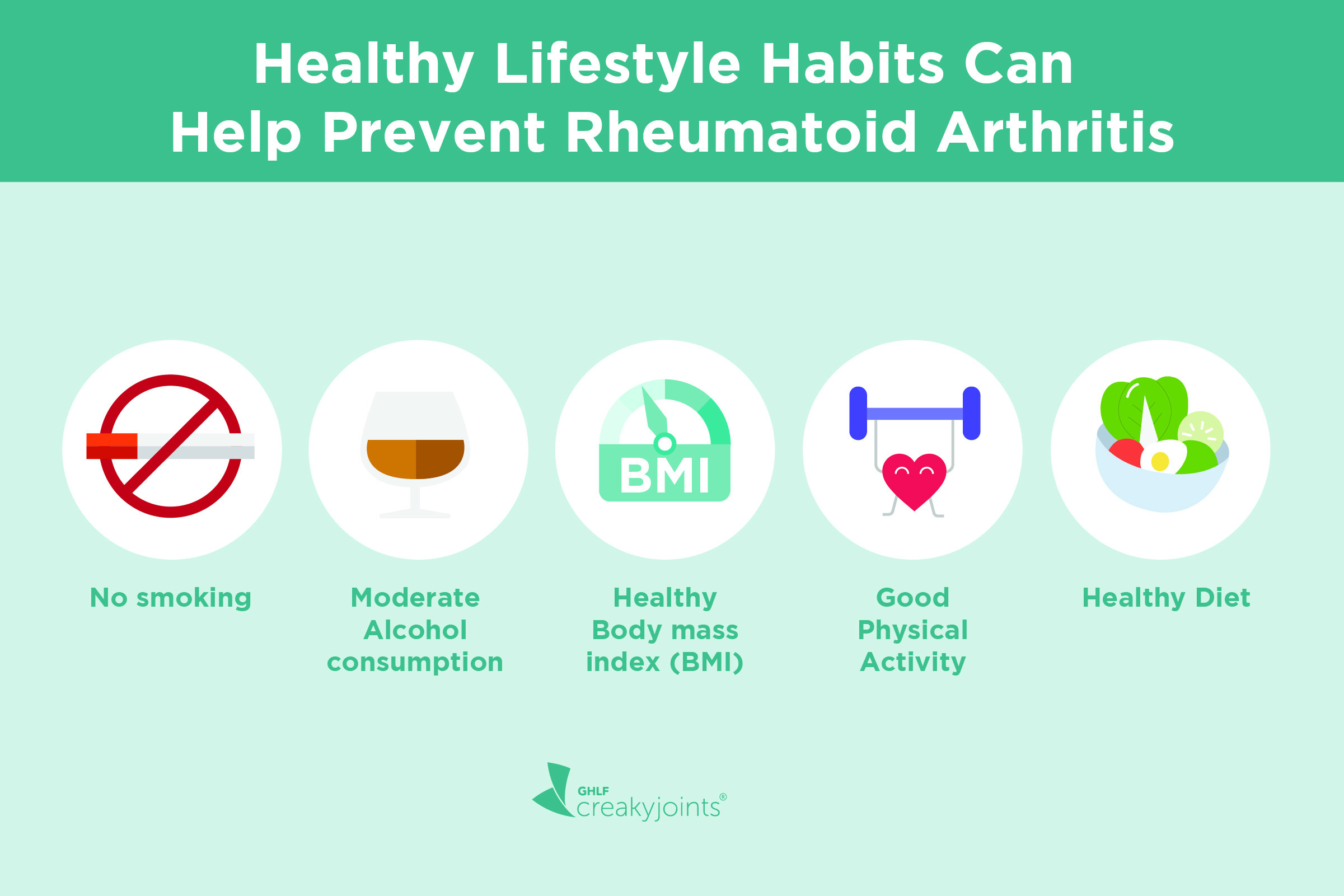
5, Arthritis Prevention.
While the development of arthritis is influenced by various factors, including genetics and age, maintaining strong bones and joint health can play a role in preventing certain types of arthritis, such as osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Here's how adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, along with other lifestyle factors, can contribute to arthritis prevention:
Bone Health: Adequate calcium intake is essential for maintaining bone health and preventing conditions like osteoporosis. Strong bones provide a solid foundation for the joints, reducing the risk of joint damage and the development of arthritis.
Joint Health: Vitamin D plays a role in joint health and can potentially contribute to the prevention of arthritis. It has anti-inflammatory effects and helps modulate the immune system, which may be beneficial in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
Cartilage Support: Calcium and vitamin D indirectly support the health of cartilage, the flexible connective tissue that cushions the joints. While they don't directly affect cartilage, they help maintain bone density and strength, which is vital for overall joint health.
Exercise and Weight Management: Regular exercise, including weight-bearing activities like walking or strength training, can help improve joint health and maintain a healthy weight. Excess weight puts additional stress on the joints, increasing the risk of joint damage and arthritis. Calcium and vitamin D support bone health, which is crucial for maintaining an active lifestyle.
Overall Nutritional Balance: A well-balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrients is important for overall health, including joint health. In addition to calcium and vitamin D, consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can provide the necessary nutrients for optimal joint function and support.
While calcium and vitamin D are important components, it's essential to adopt a comprehensive approach to arthritis prevention. This includes regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding excessive joint stress, managing chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension, and seeking medical advice for any joint-related concerns.
If you have specific concerns or a family history of arthritis, it's recommended to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide personalized guidance and recommendations for arthritis prevention strategies based on your individual circumstances.
Taking care of our bones and preventing arthritis requires a proactive approach, and proper nutrition plays a key role in this endeavor. The information provided above highlights the significance of calcium and vitamin D in supporting bone health and preventing arthritis. By incorporating calcium-rich foods such as dairy products, leafy greens, and nuts, along with vitamin D-rich sources like fatty fish and fortified products, we can optimize our intake of these vital nutrients. Remember, it's always beneficial to consult with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians to ensure you are meeting your individual needs. With a well-balanced diet and a focus on calcium and vitamin D, we can promote strong bones and reduce the risk of arthritis, leading to a healthier and more active lifestyle.



Comments
Post a Comment