Vitamin E, a potent antioxidant, has long been recognized for its beneficial effects on human health. Beyond its well-known role in protecting cells from oxidative stress, Vitamin E also holds significant potential in supporting tissue healing. In this article, we will explore five helpful pieces of information about the impact of foods rich in Vitamin E for their potential antioxidant effects and their ability to aid in tissue healing. From understanding its role as an antioxidant to identifying natural food sources and considering synergistic effects with other vitamins, this knowledge will empower you to make informed dietary choices to support your body's healing processes.
1, Vitamin E as an Antioxidant.
Vitamin E is indeed a powerful antioxidant that plays a crucial role in protecting cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are highly reactive molecules that can be generated through various processes in the body, such as metabolism and exposure to environmental factors like pollution and UV radiation.
Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the body's ability to neutralize them with antioxidants. This imbalance can lead to cell damage, inflammation, and various chronic diseases.
Vitamin E, with its antioxidant properties, helps to neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress. It acts as a chain-breaking antioxidant, meaning it interrupts the damaging chain reactions initiated by free radicals, thereby protecting cell membranes, DNA, and other cellular components from oxidative damage.
In addition to its role as an antioxidant, Vitamin E also supports the body's natural healing processes. It aids in maintaining the integrity of cell membranes, which is important for the proper functioning of cells. Vitamin E has been studied for its potential benefits in various health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, cancer, neurological disorders, and age-related macular degeneration.
It's worth noting that Vitamin E is a collective term for a group of compounds called tocopherols and tocotrienols, with alpha-tocopherol being the most biologically active form. Good dietary sources of Vitamin E include nuts, seeds, vegetable oils (such as wheat germ oil and sunflower oil), spinach, and broccoli. It can also be obtained through supplementation, although it's generally recommended to obtain nutrients from a balanced diet whenever possible.
It's important to note that while Vitamin E has many potential health benefits, excessive supplementation with high doses of Vitamin E may have adverse effects. It is always best to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplementation regimen, especially if you have any existing health conditions or are taking medications.
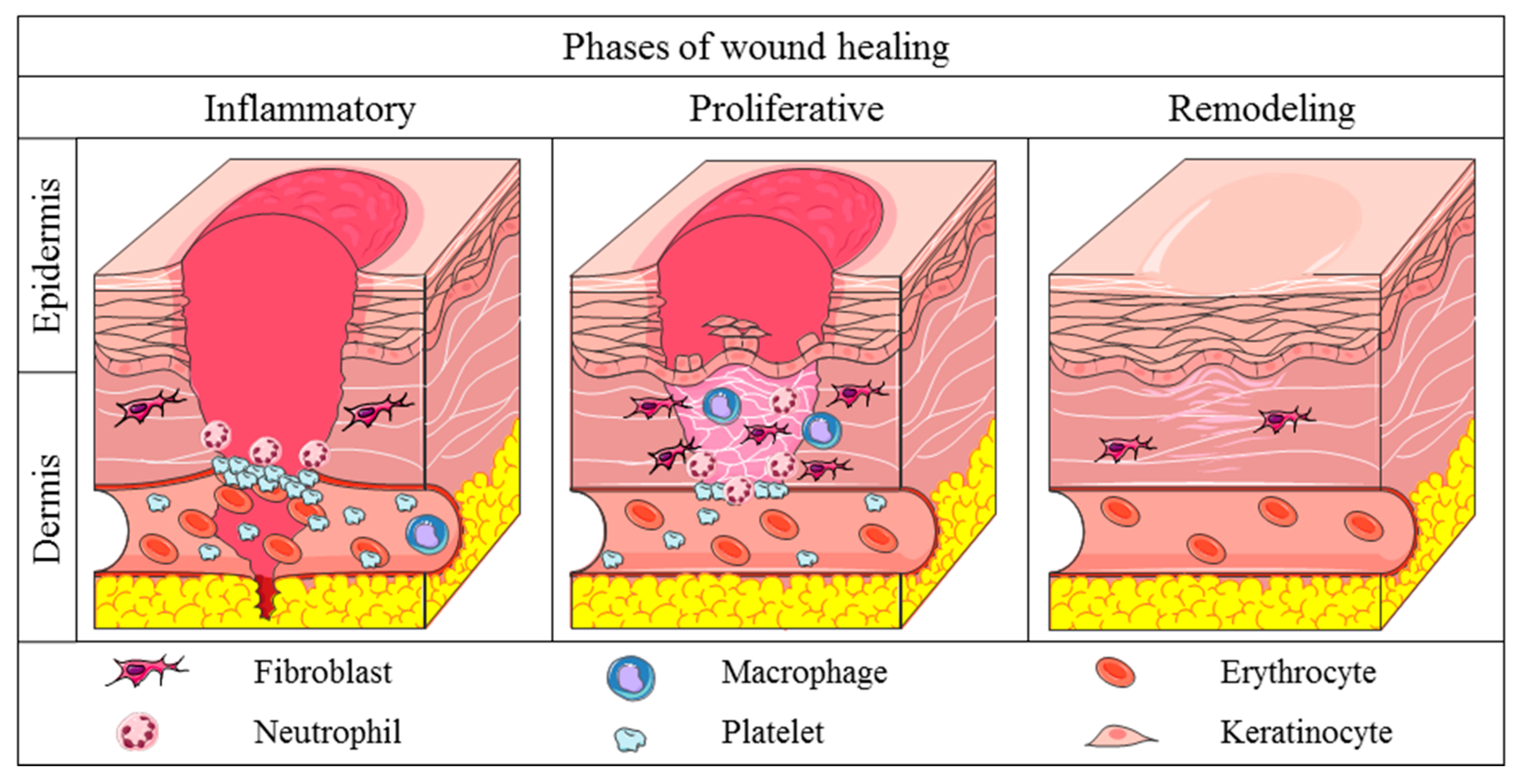
2, Tissue Healing Properties.
While Vitamin E has been studied for its potential role in tissue healing, it's important to note that the evidence regarding its effectiveness in this regard is limited and not conclusive. The role of Vitamin E in wound healing and tissue repair is still an area of ongoing research.
Vitamin E is believed to have some properties that could potentially support tissue healing. As an antioxidant, it may help protect cells from oxidative damage, which can be beneficial for tissue repair. However, the specific mechanisms through which Vitamin E promotes wound healing are not fully understood.
One proposed mechanism is its potential to stimulate the production of collagen. Collagen is a crucial protein involved in the structure and strength of tissues, including skin. Vitamin E's antioxidant properties may help protect collagen from degradation, thereby supporting tissue healing. However, more research is needed to fully understand the extent of Vitamin E's influence on collagen synthesis.
Additionally, Vitamin E is thought to promote blood circulation, which can aid in delivering oxygen and nutrients to the injured tissues. Proper blood flow is essential for the healing process as it supplies the necessary resources for tissue repair. However, the direct impact of Vitamin E on blood circulation and its role in tissue healing requires further investigation.
It's important to note that while Vitamin E may have potential benefits for tissue healing, it should not be considered a sole treatment for wounds or tissue injuries. Proper wound care, including keeping the wound clean, applying appropriate dressings, and following medical advice, is crucial for optimal healing. If you have a wound or tissue injury, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
3, Natural Food Sources.
You've mentioned some excellent food sources of Vitamin E. Including these foods in your diet can contribute to meeting your Vitamin E requirements and supporting tissue healing and overall health. Here's a list of natural food sources rich in Vitamin E:
Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, sunflower seeds, hazelnuts, peanuts, and pine nuts are all good sources of Vitamin E. Snacking on a handful of these nuts and seeds or adding them to your salads, smoothies, or trail mixes can be a great way to incorporate Vitamin E into your diet.
Vegetable Oils: Wheat germ oil, sunflower oil, safflower oil, and olive oil are known for their Vitamin E content. These oils can be used for cooking, salad dressings, or drizzling over roasted vegetables to enhance both taste and nutritional value.
Green Leafy Vegetables: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are examples of leafy greens that contain Vitamin E. Adding these greens to your salads, stir-fries, or smoothies can help increase your Vitamin E intake.
Avocado: Avocado is not only a source of healthy fats but also contains Vitamin E. Enjoy it sliced on toast, mashed in guacamole, or added to salads and sandwiches for a nutrient boost.
Other food sources that contain smaller amounts of Vitamin E include whole grains, such as wheat germ and brown rice, as well as fruits like mangoes and kiwis. Remember that Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin, so consuming these foods with a source of healthy fats can enhance its absorption.
It's worth noting that the exact amount of Vitamin E in these foods can vary depending on factors such as the variety, ripeness, and processing methods. However, incorporating a diverse range of these foods into your diet can help ensure a good intake of Vitamin E and other essential nutrients.
4, Synergistic Effects with Vitamin C.
Vitamin E and Vitamin C are both powerful antioxidants that work synergistically to enhance each other's antioxidant effects. They play complementary roles in protecting cells and tissues from oxidative damage caused by free radicals.
One way in which Vitamin E and Vitamin C work together is by regenerating each other. When Vitamin E neutralizes a free radical, it becomes oxidized in the process. However, Vitamin C can help regenerate the oxidized form of Vitamin E back to its active antioxidant form. This regeneration process allows Vitamin E to continue its antioxidant activity, providing prolonged protection to cells and tissues.
Moreover, Vitamin C can enhance the antioxidant properties of Vitamin E by reducing the oxidized form of Vitamin E back to its active form. This interaction helps maintain a steady supply of active Vitamin E, which is crucial for its effectiveness in neutralizing free radicals and protecting against oxidative stress.
Including foods rich in both Vitamin E and Vitamin C in your diet can provide a synergistic effect, maximizing the antioxidant benefits. Some common food sources of Vitamin C include citrus fruits (such as oranges and grapefruits), strawberries, kiwis, bell peppers, and leafy green vegetables like spinach and kale. By incorporating these foods along with Vitamin E-rich sources, you can support tissue healing and overall health by harnessing the combined antioxidant power of both vitamins.
It's important to note that a balanced and varied diet is key to obtaining a wide range of nutrients, including Vitamin E and Vitamin C. Additionally, it's always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized advice on meeting your nutritional needs.
5, Recommended Daily Intake.
The recommended daily intake (RDI) of Vitamin E for adults is approximately 15 milligrams (mg) or 22.4 international units (IU). However, it's important to note that the specific recommendations may vary slightly depending on the source and country.
The RDIs for nutrients are set to meet the needs of most healthy individuals within a specific population group. Individual requirements may vary based on factors such as age, sex, pregnancy or lactation, overall health, and specific medical conditions. For instance, certain medical conditions or medications may increase the need for Vitamin E, and in such cases, a healthcare professional's advice should be sought.
While it's important to meet the recommended intake of Vitamin E, it is generally recommended to obtain nutrients from a balanced diet rather than relying solely on supplements. Whole foods provide a broader range of nutrients, including other beneficial compounds, such as phytochemicals and dietary fiber, that work together synergistically. Additionally, consuming Vitamin E-rich foods as part of a balanced diet ensures a diverse intake of other essential nutrients.
If you have concerns about meeting your Vitamin E requirements or are considering supplementation, it's always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian who can provide personalized advice based on your specific needs and circumstances. They can help determine if supplementation is necessary and guide you on the appropriate dosage.
Incorporating foods rich in Vitamin E into your daily diet can have a profound impact on your health and well-being, particularly in terms of supporting tissue healing and benefiting from their antioxidant effects. By consuming nuts and seeds, vegetable oils, leafy greens, and other Vitamin E-rich foods, you provide your body with the necessary nutrients to combat oxidative stress, stimulate collagen production, and promote the circulation of oxygen and nutrients to injured tissues. Remember, a balanced diet that includes a variety of whole foods is essential to reap the full benefits of Vitamin E and other essential nutrients. Consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized guidance on incorporating Vitamin E-rich foods into your diet and promoting optimal tissue healing. Embrace the power of Vitamin E and support your body's healing processes naturally.




Comments
Post a Comment